If you’re in business, you’ve probably heard of the term ‘Return on Sales’ (ROS). It’s a crucial financial metric that indicates how much profit a company is generating from its sales revenue. In this article, we will dive into the details of Understanding Return on Sales its importance, and how to calculate it.
What is Return on Sales (ROS)?
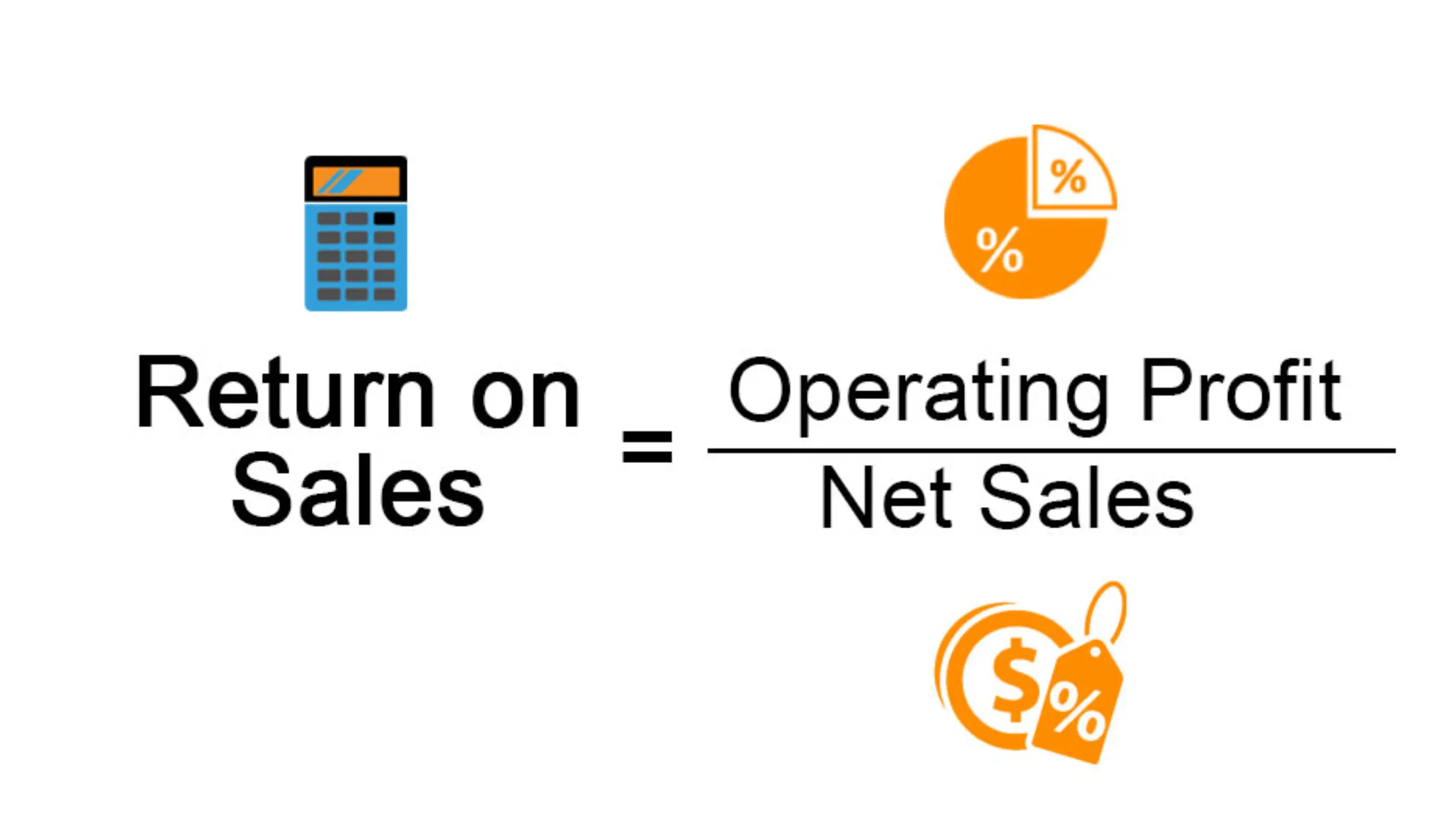
ROS, also known as Operating Profit Margin, is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability by comparing its operating profit to its net sales. It indicates how much profit a company is generating from each dollar of sales revenue.
Importance of ROS
Helps in assessing profitability
ROS is a critical metric that helps in assessing the profitability of a company. A higher ROS indicates that a company is generating more profit from its sales revenue, which is a positive sign. On the other hand, a lower ROS indicates that a company is not generating enough profit from its sales revenue, which could be a cause for concern.
Helps in evaluating performance
ROS is also a useful metric in evaluating a company’s performance. It allows companies to compare their profitability with that of their competitors or industry standards. A higher ROS than competitors or industry standards indicates that a company is performing well, while a lower ROS indicates that there is room for improvement.
Useful in making financial decisions
ROS is a crucial metric that can help in making financial decisions. For instance, if a company has a low ROS, it may need to increase its prices or reduce its expenses to improve profitability. Conversely, if a company has a high ROS, it may have room to invest more in its business or return value to its shareholders.
Calculation of Return on Sales
The formula below can be used to determine ROS:
ROS = (Operating Profit / Net Sales) x 100
Where Operating Profit is the profit generated from the company’s operations, and Net Sales are the total sales revenue generated by the company.
For example, if a company’s operating profit is $50,000, and its net sales are $500,000, its ROS would be:
ROS = ($50,000 / $500,000) x 100 = 10%
Interpreting the ROS Ratio
The ROS ratio indicates the percentage of profit generated by a company for each dollar of sales revenue. A higher ROS indicates that a company is generating more profit from its sales revenue, while a lower ROS indicates the opposite.
It’s essential to note that the interpretation of the ROS ratio varies depending on the industry. For example, a ROS of 10% may be considered low for a software company, while it may be considered high for a grocery store.
Factors Affecting ROS
Several factors can affect a company’s ROS, including:
Industry Type
Different industries have different ROS standards. For instance, industries with low-profit margins, such as grocery stores, may have lower ROS than industries with high-profit margins, such as software companies.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions, such as recessions or booms can also affect a company’s ROS. During a recession, for example, consumers may reduce their spending, which can lead to lower sales revenue and ultimately affect a company’s profitability.
Company’s Competitive Position
A company’s competitive position in the market can also affect its ROS. For instance, if a company has a high market share, it may have more pricing power, which can result in higher profit margins and a higher ROS.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ROS
Advantages
- ROS is a simple and easy-to-calculate metric that can help companies assess their profitability and make informed financial decisions.
- It can also be used to evaluate a company’s performance relative to its competitors or industry standards.
Disadvantages
- ROS does not take into account a company’s debt or taxes, which can affect its profitability.
- The interpretation of ROS varies depending on the industry, so it may not be a useful metric for comparing companies across different sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Return on Sales (ROS) is a crucial financial metric that indicates a company’s profitability by comparing its operating profit to its net sales. It helps in assessing profitability, evaluating performance, and making financial decisions. While ROS has its advantages and disadvantages, it remains a valuable metric in measuring a company’s profitability.